Virtual Private Cloud
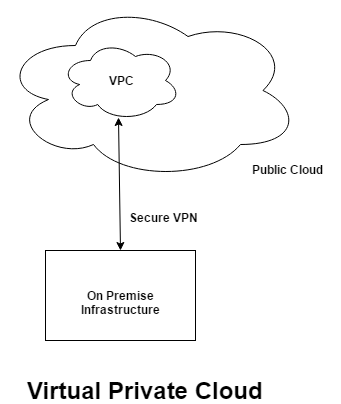
Public clouds generally offer a feature known as ‘Virtual Private Network’ or ‘Virtual Private Cloud’. Though the actual name could vary by the cloud provider, the concept remains the same.
Virtual networks in a cloud, allow the clients (or tenants) to create a logically isolated subnet, which could be considered a private network. Clients would have the flexibility to choose and assign private IP addresses as they wish in this subnet. This network could be designed to comprise of subnets, and some of these subnets could be private subnets, which are not accessible from outside world (similar to private subnets within a corporate network).
These private networks offer security and isolation and clients have greater control over the security and access policies and can customize the network topologies according to their need.
Advantages of Virtual networks:
- Assign private IP addresses
- Restrict internet access to few subnets within the virtual network
- Customize and apply security policies and access controls for resources within the network
- Gives a feel of a private datacenter on the cloud.
The virtual private network behaves like a private cloud within the public cloud and we can have connectivity from the corporate network to this private network on the cloud through VPN.
Reference Implementations:
Public Cloud providers like Amazon Webservices, Google Cloud Engine, and Microsoft Azure provide Virtual Private Cloud as a feature.